Is the “decentralization” in the blockchain ecosystem really decentralized?
When hearing about terms such as “blockchain” and “decentralization”, most of us may imagine a network system that the public can own and control collectively. But the reality is not what it seems. So let’s put the “decentralization” in our current blockchain ecosystem to test, shall we?
What is decentralization in blockchain ?
The definition of decentralization
In a blockchain, decentralization refers to the shift of control and decision-making from a centralized entity (e.g., individual, organization, or group) to a distributed network.
The aim of decentralization
Decentralized networks strive to reduce the level of trust that participants must place in one another and hinder their ability to exert authority or control over one another in ways that diminish the functionality of the network.
Why does it matter?
Decentralization is not a new concept.
In reality, decentralization is a spectrum, which all aspects of a blockchain application contain. Therefore, the more decentralized the management and resource access become, the more equitable services and rights users may obtain.
Decentralization typically has some tradeoffs, such as lower transactions per second, but ideally, the tradeoffs are worth the improved transparency, stability, and service levels they produce.
Is blockchain truly decentralized?
Blockchain on paper and in practice
Theoretically, blockchain promises a fully decentralized system where most participants do not have to place their trust in one place. For example, Ethereum is a distributed network of computers running software (i.e., nodes) to verify blocks and transaction data.
In an ideal world, every user should own and run a blockchain node, making the system completely decentralized. However, the current state of the Ethereum network does not reflect this paradigm. Here’s why:
Centralized infrastructure control more than 60% of the Ethereum nodes
According to TNW, it turns out that cloud services are hosting most of the Ethereum network, with 61.6 percent of Ethereum nodes running in the cloud.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is indirectly handling nearly a quarter of all Ethereum nodes. To put it into perspective, AWS is the most popular vendor in the cloud infrastructure services market, controlling 32 percent of the entire market.
Other centralized hosting providers include Microsoft Azure, Alibaba Cloud, Google Cloud Platform, DigitalOcean, and Hetzner.
Centralized nodes distribution
Since most cloud service providers are American-owned, the cloud nodes are not distributed evenly around the world. For example, 34 percent of Ethereum’s cloud nodes are hosted in the United States.
Check this cool dashboard with live stats for Ethereum: https://ethstats.net
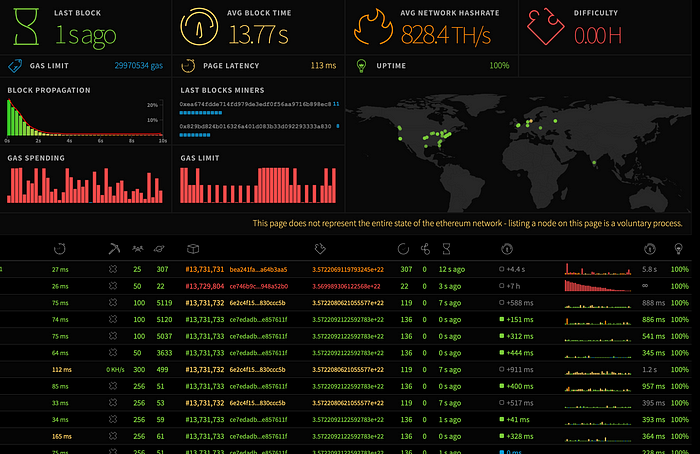
Similar situation with other cryptocurrency ecosystems
Most blockchain developers run their decentralized (Dapps) through centralized platforms, such as Alchemy and Infura. These platforms aim to manage the blockchain for the customers, so you do not have to go through the complex blockchain node setup process.
Despite that, these companies own most of the infrastructure, and users have to rely on them.
High risks due to centralized cloud service providers
When a central cloud service provider encounters a systematic issue, the result could be catastrophic. It has already happened before with the AWS outage on February 19th, 2021.
At least five cryptocurrency exchanges, including Binance, Huobi, Kucoin, BitMax, and FTX, have experienced downtime. After this incident, the promised decentralized blockchain’s reliability is questioned, and since then, attempts to transfer to alternative services have been negligible.
Is there a solution?
The difficulty of setting up a node from the users perspective
The fundamental of a genuinely decentralized ecosystem is still there: the more evenly distributed nodes, the better the whole system becomes. However, accessing the blockchain without a provider requires deep technical expertise and computer resources, taking days to set up. The process is even more complicated and demanding for users with sufficient hardware requirements but not having the necessary technical knowledge and skills.
Our solution — OMNIA
By foreseeing the state of the current blockchain application network, we have committed to preparing, researching, and applying our technical expertise to our latest project, OMNIA Protocol.
Omnia Protocol is a decentralized infrastructure protocol for securely accessing the blockchain so that no single point of failure will ever disrupt blockchain applications or wallets integrating with it.
OMNIA’s solution is truly decentralized and requires zero technical knowledge. Therefore, all users can set up access to decentralized nodes with little time and effort.
Learn more about the technological marvel behind OMNIA Protocol by following our Medium, or reading our whitepaper.